On this page:
- Records Management Training and Consultation
- Maintaining University Records in your Unit
- Determining if University Records are eligible for Permanent Retention in the Archives
- Responsible University Records Destruction
Records Management Training and Consultation
Orientation Videos About Records Management at U of T
Watch these short online orientation videos for an introduction to the key records management processes and responsibilities at the University of Toronto.
Key audiences: Anyone starting a new role or taking on new administrative responsibilities at U of T including business officers, folks supervising staff or student work, graduate student administrators, new committee or working group chairs, senior leadership team members, etc.
Request Support from a UTARMS Records Archivist
UTARMS’ Records Archivist(s) are available to provide direct support for University Records maintenance in one-on-one, team, or working group sessions. Contact us to request a presentation or friendly chat to learn more about:
- Good University Records maintenance techniques for your role, and/or unit
- Retention and disposition rules for specific University Records types within the Records Retention and Disposition Directory
- How to properly destroy University Records
- Identifying and preparing records for appraisal and transfer to the University Archives
- Maintaining records continuity during retirements/terminations/offboarding
- Setting up and maintaining good records keeping environments
- Planning for data retention and disposition
- Accessing your units’ archived records at UTARMS
Information Maintenance and Governance Partner Units
UTARMS’ records management requirements come from various programs, policy and procedures across the University of Toronto’s information landscape. UTARMS partners with the following units to develop our program and guidelines in alignment with the broader information privacy, security, resource management, and data governance requirements at U of T:
Maintaining University Records in your Unit
University Records and Information Retention and Disposition at U of T
All information, documents, email, digital files, websites, publications, reports, etc. created or collected in the course of work at the University of Toronto constitute records that require intentional maintenance and proper disposition.
Each U of T Staff, Faculty, and Librarian is responsible to purposefully retain and properly dispose of the University Records they create according to all relevant U of T Policy and Procedures and remain responsible for their maintenance until they are properly disposed.
The retention rules and disposition instructions for specific University Records types are described in the University Records Retention and Disposition Directory. For more information about using the Directory, or help locating rules for specific records types, contact UTARMS.
University records in draft, backups, duplicate or convenience copies, and reference materials are retained by their creator or collector until no longer useful according to their unit’s operational requirements, and then securely destroyed. Except for records documenting the transfer of property, and contracts signed in ink, if the same University records exist in both paper and electronic formats, the creator unit decides which version to retain and dispose of as the actionable copy and destroys the other version as a convenience copy.
Personal content, including non-work-related correspondence, students’ work, most Faculty research, and teaching materials belong to their individual creators and are therefore, those creators’ own responsibility to maintain. Where personal records have been left behind or abandoned, reasonable effort should be made to return them to their creators. For help determining whether abandoned records should be treated as personal or University Records, contact UTARMS.
Keeping Up With Disposition Responsibilities
UTARMS recommends all units review their various paper and digital records storage systems for records disposition opportunities on a regular basis and at a minimum, once every 2 years.
Records may be regularly disposed of in annual clean-up projects, in batches according to shorter intervals, and individually as part of regular workflows.
Units should maintain central administrative files to document their disposition activities including:
- Copies of appraisal statements provided by UTARMS which document University Records transfers to the Archives
- Completed and signed destruction forms,
- When using a secure destruction vendor, copies of supplied certificates or confirmations of complete and secure destruction. See also, Documenting Proper University Records Destruction Activities
Digitizing Paper University Records
UTARMS generally discourages digitizing paper University Records unless the records are required to be accessed, shared, or reconciled as part of frequent and ongoing workflows.
Paper University Records that have met their scheduled in-unit retention requirements rarely warrant the effort and expense required to ensure the digitized copies remain accessible, actionable, and secure.
Units are responsible for researching all University of Toronto information governance requirements relevant to their digitization project plans and for maintaining any digitized University Records according to the same retention and disposition requirements that apply to paper originals.
Email, Chat Threads, and Content Management Systems
When the content of an email, chat, or database/content management system, constitutes a University Record (see: University Records and information retention and disposition at U of T), the U of T Staff, Faculty or Librarian who created or collected the record is responsible to maintain and dispose of that content according to the retention and disposition rules that apply to the record type the content represents.
When University Records occur or accumulate in systems such as email inboxes, chat threads, or websites that make it difficult to control and manage the retention requirements that apply to those records, U of T Staff, Faculty, and Librarians are responsible to save the University Records content in a format or system that permits them to maintain and dispose of that content according to the retention and disposition rules that apply to the record type the content represents. This may require copying the relevant content to formats or systems that capture the content sufficiently to retain the records for their scheduled durations.
University of Toronto Websites
UTARMS has a web archiving program available to select and capture University website content accordingly. See:UTARMS Web Archiving
Protocols for IT Systems and Data Sensitivity Levels
Each U of T Staff, Faculty, and Librarian is responsible for maintaining and disposing their University Records and information according to the rules set out in the retention schedules found within the Records Retention and Disposition Directory, as well as any privacy, security, or resource management requirements that may also apply to the data or systems that make up and house University Records.
Data and system-level protocols that affect information retention should accommodate U of T Staff, Faculty and Librarians’ ability to retain and dispose of any University Records according to the rules and instructions in retention schedules.
Where sensitivity, security, or resource management protocols call for data or information alteration or destruction, the records creator or collector remains responsible for ensuring any University Records generated using that data, or housed in those systems, remain accessible for the relevant durations described in the Records Retention and Disposition Directory. This may require the record creator to save a copy in another system, or contact UTARMS to determine if a record may be disposed before it's in-office retention requirements have been met.
University Records Retention and Disposition Directory
The retention rules and disposition instructions for specific University Records types are described in the University Records Retention and Disposition Directory. For more information about using the Directory, or help locating rules for specific records types, contact UTARMS
Determining if University Records are eligible for Permanent Retention in the Archives
Once University Records have met their in-unit retention requirements, they should be properly disposed of according to the appropriate retention and disposition schedule within the Records Retention and Disposition Directory. If your office has records that have not been scheduled, please contact UTARMS before proceeding with any further disposition.
Request a Transfer
To initiate a records transfer of University Records to the archives, complete a UTARMS University Records Transfer Request Form and email a copy to the Records Archivist for review and appraisal.
The Records Archivist will review the listing to confirm the eligibility of records for transfer and be in touch with further instructions.
Preparing Paper Records for Transfer and Pick Up
In instances where you are confident most of your records are eligible for transfer; it may be convenient to pack your records as you complete your UTARMS Transfer Request Form. However, only confirmed records may be physically transferred to UTARMS so be prepared to weed or repack boxes as necessary.
To pack records for transfer:
- Separate records to be transferred, as specified in the retention and disposition schedules and follow up information from the Records Archivist.
-
Pack records in standard 1 cubic foot boxes. Units are responsible to source and purchase the appropriate boxes through their regular supply ordering process. The University Archives will not accept receipt of records packed in any other type of container.

- Place records within each storage box in the same order specified on the file list and remove any hanging file folders. Please make good use of space in each box but ensure records can be easily read and removed.
- Number each box consecutively (Box 1, Box 2, Box 3, ... until the last box), by writing the box number in bold figures on two sides of the outside of each box and ensure the box numbers coincide with those indicated on the transfer list.
- Cover each box with an appropriately fitted lid and house packed boxes in a secure space while you await your pick-up.
Preparing Digital Records for Transfer to UTARMS
Once the Transfer Request Form has been reviewed, UTARMS staff will follow-up by email with further instructions that best suit your transfer. The transfer method will depend on the amount and size of files being transferred and their location. The three most common storage locations are:
- local storage (e.g. on a computer, hard drive, or network drive)
- Sharepoint
- OneDrive
Files on local storage
- You’ll receive an email with NextCloud links to two shared folders: DOCUMENTATION and FILES.
- DOCUMENTATION is a space for any notes or comments that should be included about the digital records that are being transferred to UTARMS. Uploads may include file lists, images/screenshots of file structure, or a general description of the types of files being transferred.
- FILES is the space designated for the digital records that will be transferred to UTARMS.
- DOCUMENTATION upload
- Drag the file(s) into the browser window
- Keep the window open until you see the file(s) listed under Uploaded files
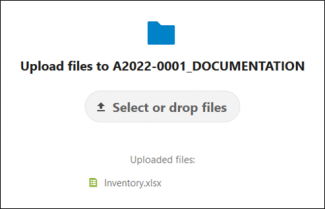
- FILES upload
- On your computer, select all the files and folders you’d like to upload (CTRL+A) and right-click and scroll to Send to > Compressed (zipped) folder
- Drag the .zip file(s) into the browser window
- Total upload size cannot exceed 6 GB.

- Once the upload process is complete, notify UTARMS for review. When UTARMS has successfully retrieved the records, you'll receive an email confirmation along with a spreadsheet inventory of what was received.
- At this point you may destroy your copy of the digital records.
- Retaining copies of records that have been transferred to the UTARMS poses potential security risks, and compromises the authenticity and reliability of the digital records that have been transferred to UTARMS.
Files in Sharepoint
-
In Sharepoint, export a file listing of the folders/files
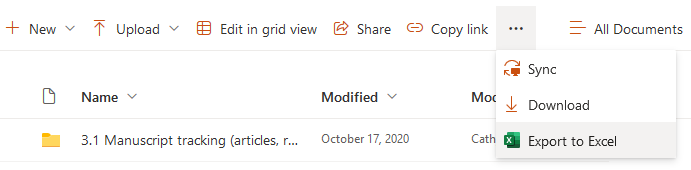
- Share folder with the Digital Records Archivist, Emily Sommers, e.sommers@utoronto.ca and email the exported file listing.
- The Digital Records Archivist will sync a copy of the files to UTARMS’ storage space. Once complete, you’ll receive an email confirmation along with a spreadsheet inventory of what was received.
- At this point you may destroy your copy of the digital records.
- Retaining copies of records that have been transferred to the UTARMS poses potential security risks, and compromises the authenticity and reliability of the digital records that have been transferred to UTARMS.
Files in OneDrive
- Share folder with the Digital Records Archivist, Emily Sommers, e.sommers@utoronto.ca.
- The Digital Records Archivist will sync a copy of the files to UTARMS’ storage space. Once complete, you’ll receive an email confirmation along with a spreadsheet inventory of what was received.
- At this point you may destroy your copy of the digital records.
- Retaining copies of records that have been transferred to the UTARMS poses potential security risks, and compromises the authenticity and reliability of the digital records that have been transferred to UTARMS.
UTARMS University Records Transfer Request Form
Responsible University Records Destruction
UTARMS recommends all units review their various paper and digital records storage systems for records disposition opportunities on a regular basis and at a minimum, once every 2 years. University Records retention and disposition requirements are documented in the Records Retention and Disposition Directory. For more information about using the Directory, or help locating rules for specific records types, contact UTARMS.
Determining if University Records are eligible for destruction
- Determine the type and date range of the University Records you are considering for destruction.
- Locate the relevant retention rules and disposition instructions for your University Records types in the Records Retention and Disposition Directory.
- Read the retention duration rule.
- University Records are ready for destruction when sufficient time has passed that the date of last activity on the records in question is equal to or greater than the amount of time listed in the retention rule for that records’ type.
- Some retention rules rely on conditions or terms having been met as opposed to specific amounts of time having passed. These rules are identified as “indefinite” in the schedules and for these records types, you may also need to consider the content or terms associated with some University Records as opposed to dates or time passed.
- Read the disposition instruction. Records eligible for destruction include a disposition instruction of “destroy.” If your records are eligible for destruction proceed to step 5. If the instruction is other than destroy, reserve the records and follow the alternate instructions.
- Document your destruction activities by listing the records types, date ranges, retention codes references and your unit’s information on a Destruction Form.
- Destroy your records according to your unit’s regular destruction procedures. Most University Records scheduled for destruction require secure and complete destruction. Open and non-sensitive information, however, can be recycled according to your unit’s recycling practices.
- File the completed Records Destruction form, along with any certificates or confirmations of destruction you may receive from shredding vendors in your central administrative records for Records Maintenance.
University Records that do not require documentation to destroy
University Records in draft, backups, duplicate or convenience copies, and reference materials are retained by their creator or collector until no longer useful according to their unit’s operational requirements, and then securely destroyed.
Records duplicated in both paper and digital formats
Except for records documenting the transfer of property, and contracts signed in ink, if the same University Records exist in both paper and electronic formats, the creator unit decides which version to retain and dispose of as the actionable copy and destroys the other version as a convenience copy. (See also: Digitizing paper University Records).
Records that are not “University Records”
Personal content, including non-work-related correspondence, students’ work, most Faculty research, and teaching materials belong to their individual creators and are therefore, those creators’ own responsibility to maintain. Where personal records have been left behind or abandoned, reasonable effort should be made to return them to their creators. For help determining responsibility for abandoned records, contact the Records Archivist.
Secure and Complete Destruction
Units are responsible for completing destruction using a method appropriate for the content of the records. When records contain internal or confidential information, they should be destroyed using an in-unit shredding machine or shredding vendor service.
If procuring a shredding vendor service, UTARMS recommends requesting a certificate or confirmation of the complete and secure destruction of the records.
Certificates and confirmations of destruction should be filed in your unit’s central administrative records for records management along with your completed Destruction Form.
Documenting Proper University Records Destruction Activities
- Document your destruction activities by listing the record types, date ranges, retention codes references and your unit’s information on a Destruction Form.
- File the completed Records Destruction form, along with any certificates or confirmations of destruction you may receive from shredding vendors in your central administrative records for Records Maintenance.